I am a Doctoral Researcher with over seven years of experience in machine learning and computer vision, specializing in the pre-training and fine-tuning of Vision–Language Models (VLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for fine-grained visual understanding. My research focuses on developing efficient multimodal representation learning frameworks that perform reliably under domain shift, limited labeled data, noisy inputs, and compute constraints. I have contributed to industry- and government-funded projects supported by the Department of Defense (DoD), FBI, Qualcomm, and the National Science Foundation (NSF), and have published in leading venues including WACV, BMVC, TAES, and TBIOM. My broader research interests include multimodal representation learning, foundation models, continual learning, and weakly- and self-supervised fine-tuning.
As I near the completion of my Ph.D., I am actively seeking opportunities for postdoctoral research and research scientist positions.
🔥 News
- 2025.11: 🎉 One paper published at BMVC 2025.
- 2025.03: 🎉 One journal published at IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems (TAES).
- 2024.09: 🎉 One paper published at WACV 2025.
- 2024.09: 🎉 One journal published at IEEE Transactions on Biometrics, Behavior, and Identity Science (TBIOM).
- 2023.12: 🎉 One journal published at IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems (TAES).
- 2023.10: 🎉 One paper published at WACV 2024.
- 2023.06: 🎉 One paper published at IJCB 2023.
- 2023.04: 🔥 Attended EAB and CITeR Biometrics Workshop in Martigny, Switzerland, organized by European Association for Biometrics (EAB).
- 2023.01: 🎉 One journal published at IET Biometrics journal.
- 2022.11: 🔥 I received the best poster award in CITer Fall Program Review.
- 2021.06: 🔥 I joined the Deep Learning Lab at WVU to work under Prof. Nasser Nasrabadi as a PhD researcher!
- 2021.04: 🎉 One journal published at IET Computer Vision.
- 2020.09: 🔥 I defended my M.Sc. thesis at IICT, BUET. Thanks to Dr. Hossen Asiful Mustafa for your invaluable supervision.
📖 Educations
2021.16 - present
- PhD in Computer Engineering, West Virginia University (WVU)
- Advisor: Dr. Nasser M. Nasrabadi, Professor, LCSEE, WVU
2014.10 - 2020.09
- M.Sc. in Information and Communication Technology (ICT), Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET)
- Thesis: View Invariant Gait Recognition for Person Re-Identification in a Multi Surveillance Camera Environment [HTML], [Code]
- Advisor: Dr. Hossen Asiful Mustafa, Professor, IICT, BUET
2008.12 - 2013.09
- B.Sc. in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Khulna University of Engineering and Technology (KUET)
💻 Research Experiences
- Research Collaboration: O Analytics, October, 2023 - Present
- Graduate Researcher: West Virginia University (WVU), June 2021 - Present
- Faculty Member: Manarat International University (MIU), Dept. of CSE, May 2019 - June 2021
- Computer Vision Researcher: Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET), March 2019 - June 2020
- Deep Learning Engineer: AIBangla, Dhaka, Bangladesh, January 2018 - February 2019
- Adjunct Faculty Member: Manarat International University (MIU), Dept. of CSE, October 2016 - April 2019
📝 Publications
📚 Vision-Language Modeling
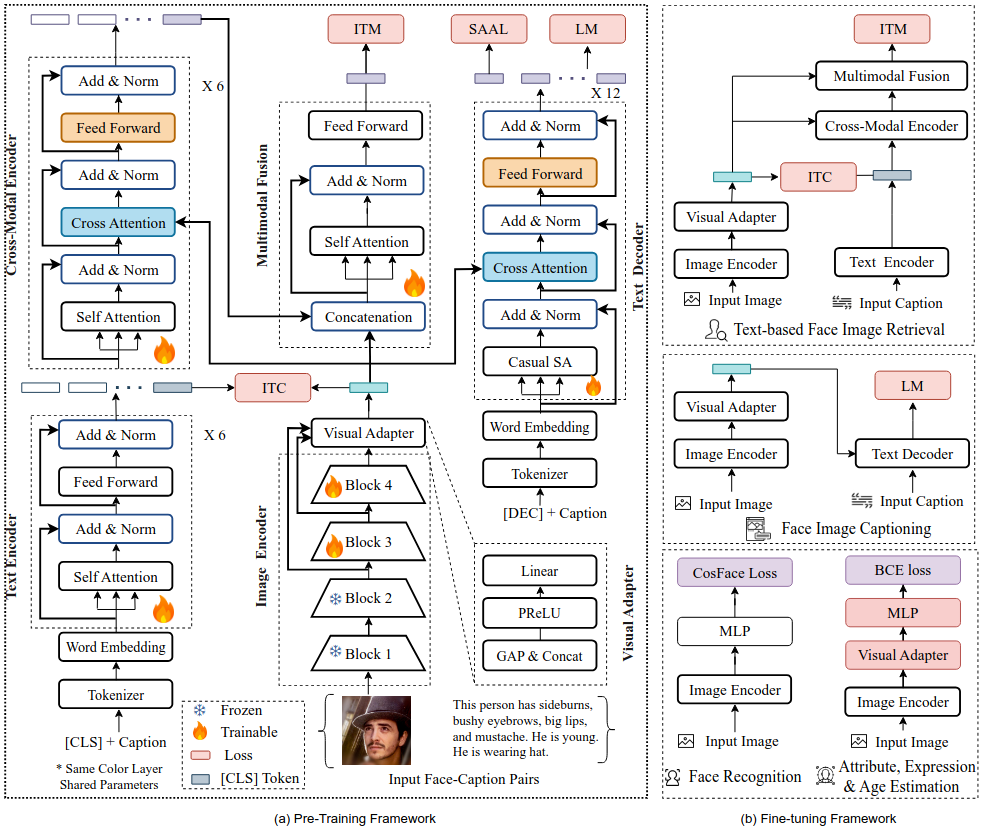
FaceCPT: Toward Cross-Modal Facial Representation Learning with Face-Caption Pre-Training
36th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC) 2025
Md Mahedi Hasan, Shoaib Meraj Sami, Nasser Nasrabadi, and Jeremy Dawson [PDF] [CODE]
Abstract
Facial representation learning (FRL) through weakly-supervised pre-training has shown significant promise across various downstream tasks, highlighting its improved generalizability. However, most existing FRL models excel only in face generation and analysis, and there is a lack of models that address cross-modal tasks. To fill this gap, we pose the following question: Can we learn a universal facial representation by pre-training on web-sourced face-caption pairs for surveillance-related tasks? These tasks include both cross-modal understanding, such as face captioning and text-based face image retrieval, as well as face analysis tasks like face, attribute, expression recognition, and age estimation. In this paper, we take a step toward this objective by introducing FaceCPT, a new framework for learning facial representation using Face Caption Pre-Training. However, domain misalignment and information asymmetry between image-text pairs challenge the model’s ability to achieve a meaningful interaction. To overcome this, we utilize contrastive learning along with a semantic attribute-aware loss (SAAL) to improve the semantic associations between face-caption pairs and encourage the model to focus on key semantic attributes, respectively. Experiments show that FaceCPT outperforms existing vision-language pre-training and FRL baselines, achieving state-of-the-art results in task-specific fine-tuning and improved zero-shot transferability across both single-modal and cross-modal tasks, even with low-resolution inputs.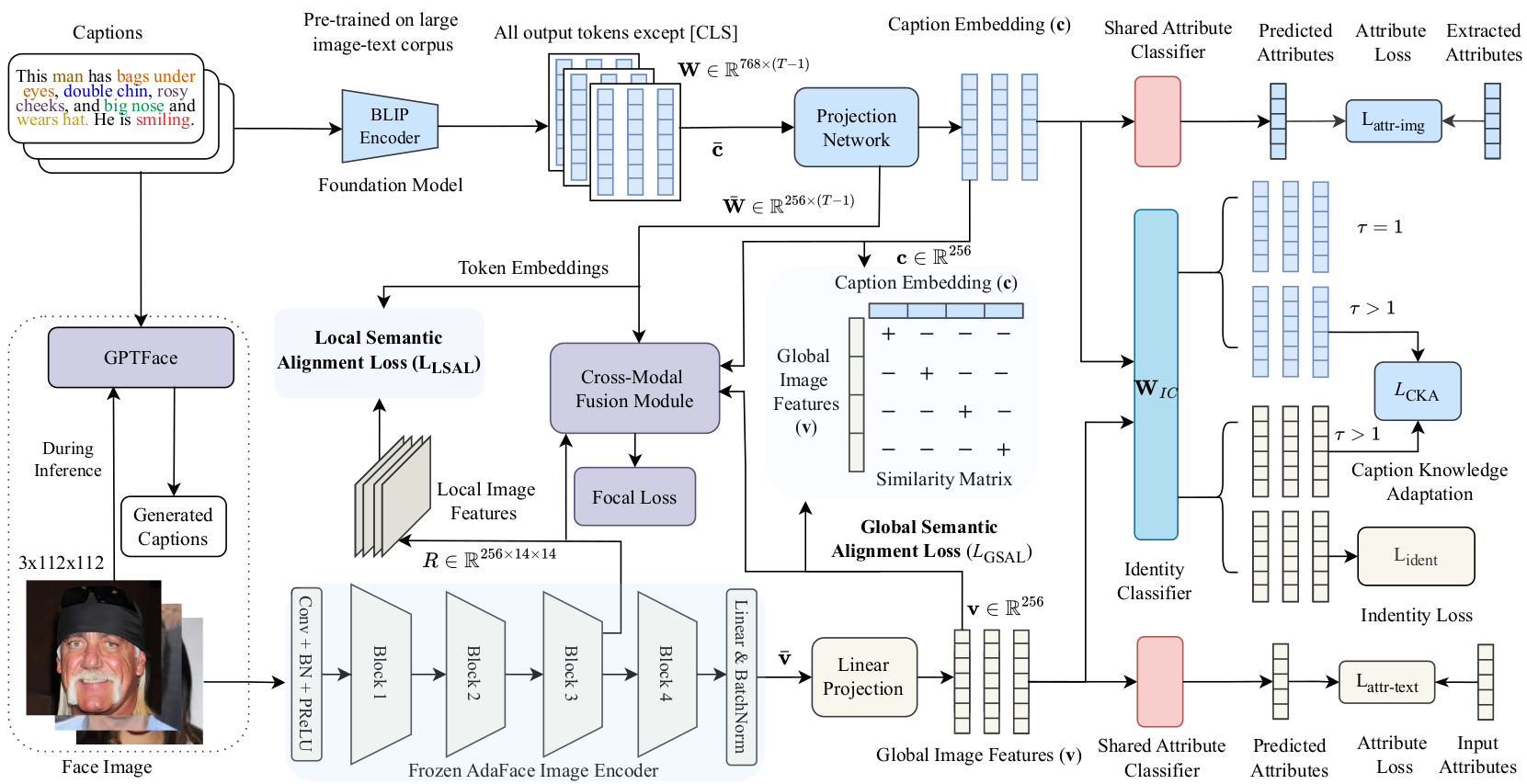
Learning Multi-Scale Knowledge-Guided Features for Text-Guided Face Recognition
IEEE Transactions on Biometrics, Behavior, and Identity Science (TBIOM)
Md Mahedi Hasan, Shoaib Meraj Sami, Nasser Nasrabadi, and Jeremy Dawson [HTML] [PDF] [CODE]
Abstract
Text-guided face recognition (TGFR) aims to improve the performance of state-of-the-art face recognition (FR) algorithms by incorporating auxiliary information, such as distinct facial marks and attributes, provided as natural language descriptions. Current TGFR algorithms have been proven to be highly effective in addressing performance drops in state-of-the-art FR models, particularly in scenarios involving sensor noise, low resolution, and turbulence effects. Although existing methods explore various algorithms using different cross-modal alignment and fusion techniques, they encounter practical limitations in real-world applications. For example, during inference, textual descriptions associated with face images may be missing, lacking crucial details, or incorrect. Furthermore, the presence of inherent modality heterogeneity poses a significant challenge in achieving effective cross-modal alignment. To address these challenges, we introduce CaptionFace, a TGFR framework that integrates GPTFace, a face image captioning model designed to generate context-rich natural language descriptions from low-resolution facial images. By leveraging GPTFace, we overcome the issue of missing textual descriptions, expanding the applicability of CaptionFace to single-modal FR datasets. Additionally, we introduce a multi-scale feature alignment (MSFA) module to ensure semantic alignment between face-caption pairs at different granularities. Furthermore, we introduce an attribute-aware loss and perform knowledge adaptation to specifically adapt textual knowledge from facial features. Extensive experiments on three face-caption datasets and various unconstrained single-modal benchmark datasets demonstrate that CaptionFace significantly outperforms state-of-the-art FR models and existing TGFR approaches.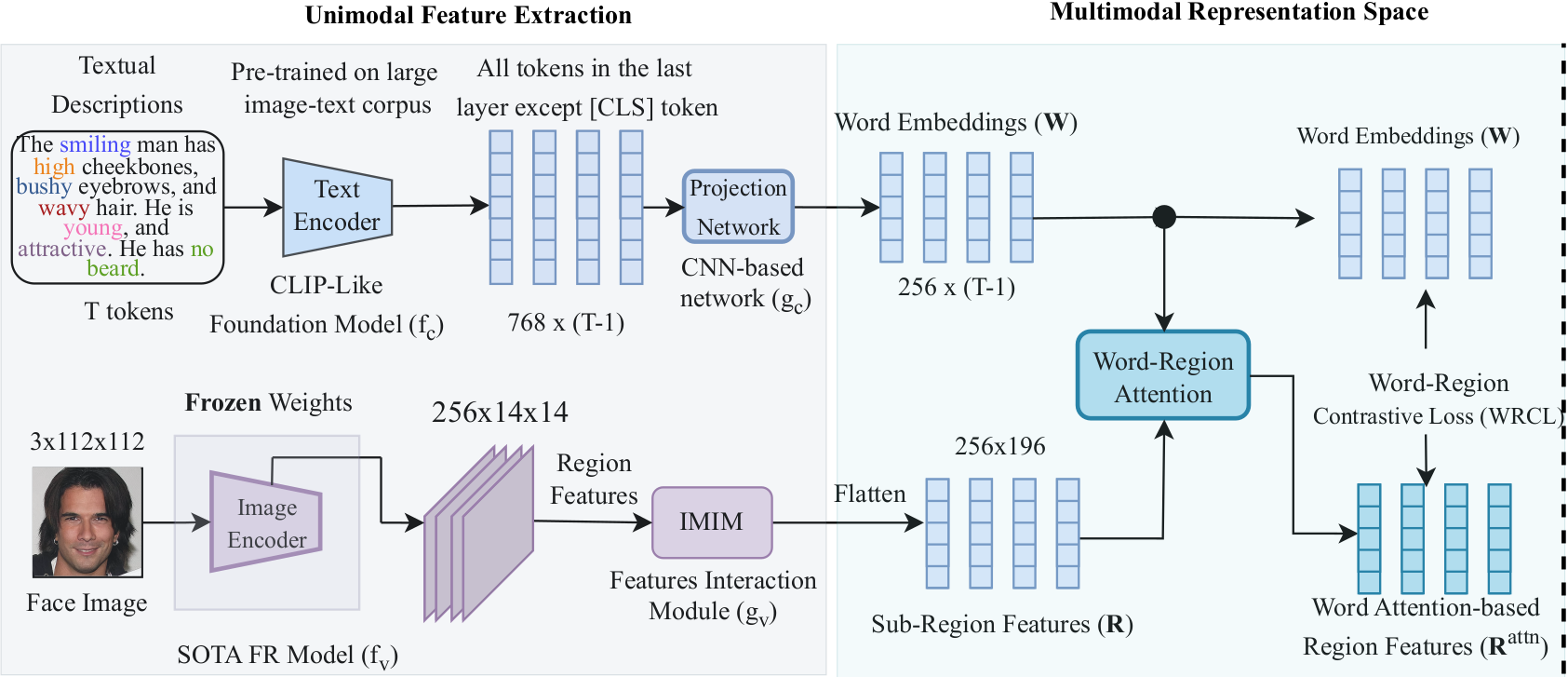
Text-Guided Face Recognition using Multi-Granularity Cross-Modal Contrastive Learning
IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV 2024)
Md Mahedi Hasan, Shoaib Meraj Sami, and Nasser Nasrabadi. [HTML] [PDF] [Video]
Abstract
State-of-the-art face recognition (FR) models often experience a significant performance drop when dealing with facial images in surveillance scenarios where images are in low quality and often corrupted with noise. Leveraging facial characteristics, such as freckles, scars, gender, and ethnicity, becomes highly beneficial in improving FR performance in such scenarios. In this paper, we introduce text-guided face recognition (TGFR) to analyze the impact of integrating facial attributes in the form of natural language descriptions. We hypothesize that adding semantic information into the loop can significantly improve the image understanding capability of an FR algorithm compared to other soft biometrics. However, learning a discriminative joint embedding within the multimodal space poses a considerable challenge due to the semantic gap in the unaligned image-text representations, along with the complexities arising from ambiguous and incoherent textual descriptions of the face. To address these challenges, we introduce a face-caption alignment module (FCAM), which incorporates cross-modal contrastive losses across multiple granularities to maximize the mutual information between local and global features of the face-caption pair. Within FCAM, we refine both facial and textual features for learning aligned and discriminative features. We also design a face-caption fusion module (FCFM) that applies fine-grained interactions and coarse-grained associations among cross-modal features. Through extensive experiments conducted on three face-caption datasets, proposed TGFR demonstrates remarkable improvements, particularly on low-quality images, over existing FR models and outperforms other related methods and benchmarks.📚 Continual Learning
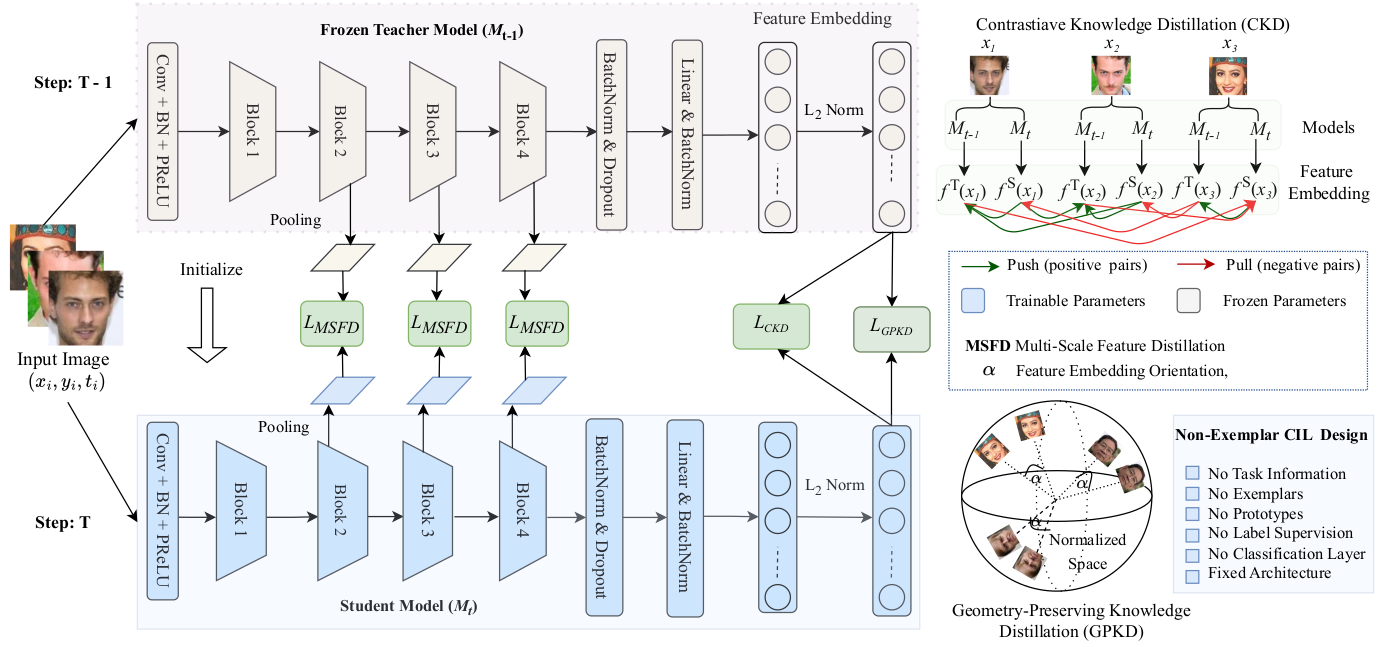
CLFace: A Scalable and Resource-Efficient Continual Learning Framework for Lifelong Face Recognition
IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV 2025)
Md Mahedi Hasan, Shoaib Meraj Sami, Nasser Nasrabadi, and Jeremy Dawson [Arxiv] [CODE]
Abstract
An important aspect of deploying face recognition (FR) algorithms in real-world applications is their ability to learn new face identities from a continuous data stream. However, the online training of existing deep neural network-based FR algorithms, which are pre-trained offline on large-scale stationary datasets, encounter two major challenges: 1. catastrophic forgetting of previously learned identities, and 2. the need to store past data for complete retraining from scratch, leading to significant storage constraints and privacy concerns. In this paper, we introduce CLFace, a continual learning framework designed to preserve and incrementally extend the learned knowledge. CLFace eliminates the classification layer, resulting in a resource-efficient FR model that remains fixed throughout lifelong learning and provides label-free supervision to a student model, making it suitable for open-set face recognition during incremental steps. We introduce an objective function that employs feature-level distillation to reduce drift between feature maps of the student and teacher models across multiple stages. Additionally, it incorporates a geometry-preserving distillation scheme to maintain the orientation of the teacher model's feature embedding. Furthermore, a contrastive knowledge distillation is incorporated to continually enhance the discriminative power of the feature representation by matching similarities between new identities. Experiments on several benchmark FR datasets demonstrate that CLFace outperforms baseline approaches and state-of-the-art methods on unseen identities using both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets.🧑🎨 Face Recognition
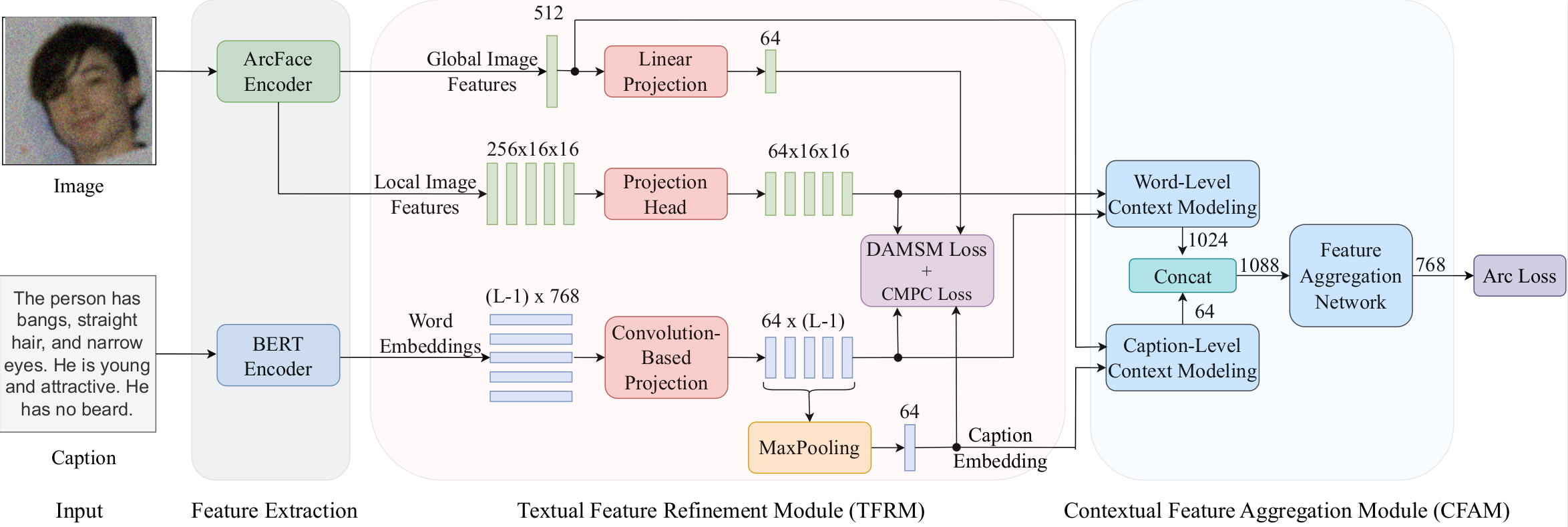
Improving Face Recognition from Caption Supervision with Multi-Granular Contextual Feature Aggregation
2023 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB 2023)
Md Mahedi Hasan, and Nasser Nasrabadi. [HTML] [PDF] [CODE]
Abstract
We introduce caption-guided face recognition (CGFR) as a new framework to improve the performance of commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) face recognition (FR) systems. In contrast to combining soft biometrics (eg., facial marks, gender, and age) with face images, in this work, we use facial descriptions provided by face examiners as a piece of auxiliary information. However, due to the heterogeneity of the modalities, improving the performance by directly fusing the textual and facial features is very challenging, as both lie in different embedding spaces. In this paper, we propose a contextual feature aggregation module (CFAM) that addresses this issue by effectively exploiting the fine-grained word-region interaction and global image-caption association. Specifically, CFAM adopts a self-attention and a cross-attention scheme for improving the intra-modality and inter-modality relationship between the image and textual features, respectively. Additionally, we design a textual feature refinement module (TFRM) that refines the textual features of the pre-trained BERT encoder by updating the contextual embeddings. This module enhances the discriminative power of textual features with a cross-modal projection loss and realigns the word and caption embeddings with visual features by incorporating a visual-semantic alignment loss. We implemented the proposed CGFR framework on two face recognition models (ArcFace and AdaFace) and evaluated its performance on the Multi-Modal CelebA-HQ dataset. Our framework significantly improves the performance of ArcFace in both 1:1 verification and 1:N identification protocol.📚 Automatic Target Recognition
-
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems (TAES 2024)FDCT: Frequency-Aware Decomposition and Cross-Modal Token-Alignment for Multi-Sensor Target Classification, Shoaib Meraj Sami, Md Mahedi Hasan, Nasser Nasrabadi, Raghuveer Rao [HTML] [PDF] -
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems (TAES 2024)Contrastive Learning and Cycle Consistency-Based Transductive Transfer Learning for Target Annotation, Shoaib Meraj Sami, Md Mahedi Hasan, Nasser Nasrabadi, Raghuveer Rao [HTML] [PDF]
📚 Fingerprint Recognition
IET Biometrics 2023On Improving Interoperability for Cross-Domain Multi-Finger Fingerprint Matching Using Coupled Adversarial Learning, Md Mahedi Hasan, Nasser Nasrabadi, and Jeremy Dawson [HTML] [PDF]BIOSIG 2022[Oral] Deep Coupled GAN-Based Score-Level Fusion for Multi-Finger Contact to Contactless Fingerprint Matching, Md Mahedi Hasan, Nasser Nasrabadi, and Jeremy Dawson [HTML] [PDF] [CODE]
📚 Gait Recognition
IET Computer Vision 2021Learning view-invariant features using stacked autoencoder for skeleton-based gait recognition, Md Mahedi Hasan, and Hossen Asiful Mustafa. [HTML] [PDF]IJCSIS 2021Multi-level feature fusion for robust pose-based gait recognition using RNN, Md Mahedi Hasan, and Hossen Asiful Mustafa. [PDF]
📚 Others
Book Chapter 2020Deep Learning based Early Detection and Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Retinal Fundus Images, Sheikh Muhammad Saiful Islam, Md Mahedi Hasan, Sohaib Abdullah arXivRAAICON 2019Robust Pose-Based Human Fall Detection using Recurrent Neural Network, Md Mahedi Hasan, Md Shamimul Islam, Sohaib AbdullahICBSLP 2018YOLO-Based Three-Stage Network for Bangla License Plate Recognition in Dhaka Metropolitan City, Sohaib Abdullah, Md Mahedi Hasan, Sheikh Muhammad Saiful Islam , [dataset]
📝 Research Projects
-
Optimizing Foundation Models for Edge Computing Platforms (2025.08 - 2028.08)
- Name of Funding Organization: Qualcomm
-
Contribution:
- Designed a Conv-LoRA–based domain adaptation technique to fine-tune the Segment Anything Model (SAM), for defect segmentation, reducing training cost by 40% and enabling edge-device deployment.
- Developing self-supervised techniques to optimize foundation models for tasks with limited manually annotated data.
-
Super-Resolution Object Characterization in Low Earth Orbit (2023.08 - 2025.05)
- Name of Funding Organization: Department of Defense (DoD)(USAF, #FA8649-23-P-0408)
-
Contribution:
- Designed an SRGAN-based super-resolution framework for diverse target chips detected and cropped by the Innovative Target Chipping (ITC) module, enhancing real-time detection of space objects.
- Developed an adapted Multi-Scale SRGAN module to perform super-resolution with up-scaling factors of 4 and 8, improving the fidelity of satellite image patches for downstream analysis.
-
A Perpetual Deep Face Recognition System (2022.09 - 2023.10)
- Name of Funding Organization: NSF (CITer, #22F-01W)
-
Contribution:
- Designed and implemented the complete research pipeline, including data preprocessing, model development, training, and evaluation.
- Built a class-incremental continual learning framework, CLFace, for face recognition that enables consistent performance improvement across sequential tasks, and mitigates catastrophic forgetting.
-
One-to-One Face Recognition with Human Examiner in the Loop (2022.05 - 2023.04)
- Name of Funding Organization: NSF (CITer, #22S-06W)
-
Contribution:
- Developed CaptionFace, a text-guided face recognition framework that enhances state-of-the-art face recognition models by integrating facial attribute information through natural language descriptions.
- Proposed GPTFace, a vision–language captioning model that combines ViT-B/16 and GPT-2 to generate semantic descriptions from low-resolution facial images, achieving a 7% improvement in zero-shot retrieval performance.
-
2023 Incomplete Fingerprint Records and Matching (2023.08, 2024.08)
- Name of Funding Organization: Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI)
-
Contribution:
- Conducted multi-finger fusion across all ten fingers using commercially off-the-shelf fingerprint matchers and performed comprehensive performance analysis.
-
Evaluation of the Performance of Multi-Finger Contactless Fingerprint Matching (2021.08, 2022.08)
- Name of Funding Organization: NSF (CITer, #21S-04W)
-
Contribution:
- Developed a Coupled-GAN–based framework to improve multi-finger contactless fingerprint matching and enhance contact-to-contactless fingerprint interoperability, achieving an 11.68% improvement in TAR at FAR = 0.01% over prior state-of-the-art methods.
📝 Datasets
-
Real-time Automatic Bangla License Plate Recognition Datasets (2018.05 - 2019.04)
- Description: We have developed a real-time automatic Bangla license plate recognition system based on YOLO-v3. Additionally, we curated a dataset comprising 1,500 diverse images of Bangladeshi vehicular license plates. These images were manually captured from streets, simulating various real-world scenarios. This project is funded by department of CSE, Manarat International University (MIU).
- Resources: [dataset], [report]
-
Deep Isolated Bangla Handwritten Basic and Compound Character Recognition Datasets (2018.01 - 2018.12)
- Description: We present AIBangla, a new benchmark image database for isolated handwritten Bangla characters with detailed usage and a performance baseline. Our dataset contains 80,403 hand-written images on 50 Bangla basic characters and 249,911 hand-written images on 171 Bangla compound characters which were written by more than 2,000 unique writers from various institutes across Bangladesh. This project is funded by department of CSE, Manarat International University (MIU)
- Resources: [dataset], [report]
-
Deep Bangla Sign Language Recognition from Video: A New Large-scale Dataset (2020.05 - 2022.05)
- Description: We have developed an attention-based Bi-GRU model that captures the temporal dynamics of pose information used by individuals communicating through sign language. Furthermore, we created a large-scale dataset called the MVBSL-W50, which comprises 50 isolated words across 13 categories.
- Resources: [dataset], [report]
🎖 Fellowships and Awards
- 2022.11 Best Poster Award: Center for Identification Technology Research (CITer) workshop, MI, USA, 2022
- 2009-2012 University Merit Scholarship: Govt. of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh
👩💻 Technical Skills
- Programming Languages: Python (expert), C++ (proficient), Java (advanced)
- DS & ML Tools (Python): NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, Seaborn, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Hugging Face
- Systems & Deployment: AWS, GCP, Kubernetes, Docker, MLflow, TorchServe, TensorRT
- ML Techniques: Deep Learning, NLP, Computer Vision, RL and Reasoning in LLMs,
- Algorithms: Multi-Modal Learning (VLMs, MLLMs) Fine-tuning & Adaptation (LoRA, Q-LoRA)
📖 Reviewing
- Conferences: Reviewer at CVPR 25, AAAI 26, WACV 24,25, BMVC 25, IJCB 23
- IEEE Transactions: Reviewer at TPAMI 25, TIP 25, TIFS 25, TASE 24, 25, TCSVT 24, 25, TPD 24
- Others: Reviewer at Pattern recognition, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence
💬 Teaching
Lecturer (2019.04 - 2021.05)
- Teaching Faculty at Manarat International University (MIU), Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE)
- Responsibilities: Conducting undergraduate classes
- CSE-437: Computer Vision and Robotics [Spring 2019], [Fall 2019]
- CSE-411: Artificial Intelligence [Summer 2019]
- CSE-433: Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems [Fall 2019]
- Supervising undergraduate student research and projects
Adjunct Lecturer (2016.06 - 2019.04)
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE), Manarat International University (MIU)
💬 Affiliations
- 2015.03 - 2021.05 Assistant Editor of Byapon Science Magazine, Office: 48/1, Motijheel C/A, Dhaka-1200, Bangladesh
- 2023.07 - Present IEEE Student Member
💬 Invited Talks
- 2025.11, Talk: “A Deep Dive into Vision Transformer and Its Multimodal AI Applications,” School of Mathematical and Data Sciences, West Virginia University (WVU), Morgantown, WV, November 2025
- 2023.10, Presentation: A Perpetual Deep Face Recognition System, Fall 2023 Program Review, organized by Center for Identification Technology Research (CITeR), Potsdam, NY, October 2023.
- 2023.03, Presentation: Deep Multi-Finger Contact-to-Contactless Fingerprint Matching for Increased Interoperability, organized by Computer Science and Electrical Engineering, WVU, March 2023.
- 2023.12, Talk: “The Engine Behind ChatGPT,” Cognitive Mind, Dhaka, Bangladesh, December 2023
- 2023.04, Presentation: Text-Guided Face Recognition using Contrastive Learning, EAB & CITeR Biometrics Workshop, organized by European Association for Biometrics (EAB), Martigny, Switzerland, April 2023.
- 2022.11, Presentation: One-to-One Face Recognition with Human Examiner in the Loop, Fall 2022 Program Review, organized by CITeR, East Lansing, MI, November 2022. [Best Poster Award]
- 2022.05, Presentation: Evaluation of the Performance of Multi-Finger Contactless Fingerprint Matching, Spring 2022 Program Review, organized by CITeR, Buffalo, NY, May 2022.


